Search Results
124 items found for ""
- Solenoids vs. HASEL
HASEL actuators are an excellent alternative to solenoids for applications that require linear motion in a compact and simple package. HASEL actuators have several advantages over solenoid actuators, but a key benefit of HASEL actuators is that they consume very little power and do not generate heat while activated. In contrast, solenoids require a continuous supply of power to hold a position and they generate a significant amount of heat. The following video illustrates this difference with thermal imaging of HASEL and solenoid actuators operating side-by-side. Below is a more detailed comparison of these two technologies that provides additional insight into the potential benefits of HASEL actuators over solenoids. Solenoids and HASEL actuators make use of two different but related fundamental branches of physics - electromagnetics and electrostatics, respectively. Solenoids rely on electromagnetic forces which are generated by applying current through a coil of wire. Typically a metal rod or plunger is located in the middle of the coil so that the electromagnetic force causes the plunger to move in a linear motion. HASEL actuators rely on electrostatic forces which are generated by applying a constant voltage to the electrodes that are separated by layers of liquid and polymer dielectrics. The resulting electric field acts on the dielectric layers which displaces the liquid dielectric and causes the overall actuator structure to change shape. Power consumption and heat generated Solenoids require constant current and power to hold a position. This limits solenoid application to those with low-duty cycles or that do not require a position to be held actively for long periods of time. Often solenoids require methods to dissipate heat which may involve passive or active cooling. On the other hand, HASEL actuators require little to no power while maintaining a position. Therefore, HASEL actuators are a better alternative for applications that require longer duty cycles, the ability to hold positions, require low power consumption, and/or are intolerant of temperature changes. Materials and Parts There are several benefits related to the materials and components used for HASEL actuators. While the coil, plunger, and case of solenoid must be made from metal, HASEL actuators can be made without any metal parts which can be beneficial for some operating environments and may reduce system weight. Additionally, HASEL actuators do not have any moving parts; the liquid-filled structure of a HASEL actuator acts as a single composite structure. Solenoids produce audible clicking sounds as parts slide and contact each other, but HASEL actuators are virtually silent during operation. HASEL actuators are not limited by a single form factor. They can be designed in a variety of different shapes and sizes to meet the needs of a specific application. Once again, the simple structure of HASEL actuators makes it easier to integrate them into different systems and structures. The flexible materials even make it possible to integrate HASEL actuators into clothing or accessories for wearable actuator applications. Push vs. Pull Similar to solenoid actuators, HASEL actuators generally provide push or pull forces only. Artimus Robotics offers contracting actuators, which pull, and expanding actuators, which push. Of course, the operation of these actuators can be modified for different types of motion. Considerations for Using HASEL Actuators When it comes to powering HASEL actuators, it is important to keep in mind that they require high voltage. In order to apply a large enough electric field, the voltage applied to HASEL actuators is typically 6 - 8 kV. However, the current is low (< 1 mA) and as a result, the actuators are safe, despite the high voltage. Proper insulation of the actuators and electronics is needed to prevent arcing to equipment or people. Experts at Artimus Robotics are able to guide on best practices for insulation and isolation of HASEL actuators for safe and successful operation. Artimus Robotics also offers specialized HV power supplies for the control and operation of HASEL actuators. Another consideration when choosing a HASEL actuator over a solenoid is the force and stroke required. Just like solenoids, the force from a HASEL actuator decreases with increasing stroke. Additionally, for a given force requirement, the footprint of a suitable HASEL actuator may be larger than that of a solenoid. You can refer to the products page for standard product performance information, but HASEL actuators can be easily customized to suit a specific application so contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com to discuss customization options. Potential Applications for HASEL Actuators over Solenoids Finally, below are a few applications where HASEL actuators provide a superior solution over solenoids: Short stroke linear motion applications that require holding position(s) for extended periods of time. Latches, diverters, and proportional valves. Especially those that have 2 or more active states that must be maintained with long duty cycles. Applications requiring linear motion without any metal or magnetic parts (e.g. MRI machine). Applications such as haptics where compliance and slim form factors are important. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Charge-Control Techniques in High Voltage Power Supplies
Artimus Robotics has developed a number of breakthroughs related to high voltage driving electronics that enable unprecedented control over HASEL actuators, as well as other electrostatic devices such as dielectric elastomer actuators, electrostatic clutches, and electroadhesive devices. In particular, Artimus has developed a method of driving HASEL actuators using a charge-controlled technique. The design utilizes optocouplers (or alternative switching elements like MOSFETs or IGBTs) that are controlled using either an analog voltage or PWM signal with a variable duty cycle. The method creates analog HV switches that are capable of controlling the amount of charge stored by the HASEL actuators, and therefore, its actuated state. The unique arrangement of switches provides precise control over the position as well as the actuation speed of the actuators during both the charging and discharging portions of an actuation cycle. These analog switches can be scaled to a nearly arbitrary number of independent actuation channels while utilizing only one centralized HV amplifier set to a constant DC output voltage, thereby enabling extremely compact electronic packages for operating large arrays of HASEL actuators. Furthermore, since the discharge mechanism of the actuators is active, not passive (like a resistor connected in parallel with the actuator, which is common in the field), the actuators maintain a ‘catch’ state, whereby they actuate and hold a position without consuming much energy. Additionally, this technique allows control of the state of actuation during discharge, which is analogous to eccentric contraction of skeletal muscles. With these breakthroughs, Artimus Robotics has become a world leader in creating compact, multi-channel HV power supplies to solve even the most difficult motion challenges using HASEL actuators. If you are curious about how Artimus Robotics can design power supplies to meet your needs, contact us directly at info@artimusrobotics.com. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Haptic Feedback with HASEL Actuators
Haptic feedback is a common way for devices to communicate with users. The vibration setting of a cell phone or video game controller is the most familiar example of traditional touch-based haptic feedback, but haptics can include visual responses such as lights or visual-touch combinations, such as those found in aircraft training simulations. The requirements for haptic actuators are increasing as applications demand more functionality. Automotive manufacturers are integrating non-visual communication systems in car seats, armrests, and steering wheels to improve Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) such as blind-spot detection (haptic cue). Medical manikin patient simulators imitate breathing, pulse, and other normal body functions but also need an abrupt signal to the medical trainee for certain reactions. AR/VR needs both human-like touch and distinguished mechanical touch for a comprehensive experience. HASEL actuators can advance the capabilities of haptic communication in these applications due to the wide bandwidth of these actuators. Not only can HASEL actuators provide vibration at high frequencies, but also they demonstrate truly organic, lifelike motion at lower frequencies. Additional benefits include silent operation and a soft-compliant structure. Further, the integration of HASEL’s intelligent self-sensing opens new capabilities and sensations in haptics that were not previously possible. Benefits of HASEL actuators as haptic devices: Fast actuation time Frequencies from 0 Hz (DC) to 100s of Hz Organic, lifelike motion Soft, compliant structure Insulated and safe for direct contact with humans Silent operation Intelligent self-sensing Industries and applications that seek delicate, human touch-like haptic feedback or a wide range of capabilities from haptic devices are finding that HASEL actuators from Artimus Robotics are the ideal solution. These include: AR/VR Robotics Smart wearable devices Assistive motion devices Smart clothing Medical manikins and patient simulators Automotive and mobility tech Gaming Aerospace and defense About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Wide bandwidth demonstration of HASEL actuators: 1 Hz to 50 Hz
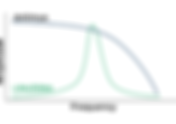
HASEL actuators from Artimus Robotics offer analog (proportional) control and wide bandwidth. These actuators can operate at 0 Hz (DC) up to 100 Hz with full actuation, and even into the hundreds of Hz with partial actuation or vibration. This bandwidth and the fast actuation speeds are powerful differentiators compared to other actuation technologies since traditional haptic actuators like eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors or linear resonance actuators (LRA) only get significant amplitude in a narrow bandwidth. The following video demonstrates the HASEL actuator at different frequencies. Please contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com to learn more. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Speed Comparison: HASEL actuator vs. pneumatic actuator
HASEL actuators from Artimus Robotics are often compared to pneumatic actuators. Two characteristics are immediately noticed in these comparisons. First, HASEL actuators operate much more quietly than pneumatic actuators since HASEL actuators emit no noise during operation. Second, HASEL actuators operate much faster than pneumatic actuators. At high frequencies, pneumatic actuators can’t move the fluid quickly enough to fully actuate or to actuate at the full speed. HASEL actuators are electrically driven and not dependent on the movement of a fluid, so they actuate at the speed of the electrical signal. This can be as fast as 5 ms in some applications. The following video demonstrates the HASEL actuator speed compared to a pneumatic actuator across a range of frequencies. Both actuators are comparable at low frequencies, but as the frequencies increase, the pneumatic actuator can’t keep up. Please contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com to learn more. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Customization of HASEL Actuators: Optimizing for Force
HASEL actuators from Artimus Robotics are extremely customizable. Not only are the actuators modular, but their design principles can be easily varied to optimize for specific applications. Recently, an automotive customer in the Artimus Partnership Program required a higher force output from a fixed-size actuator. This application didn’t need as much stroke, so Artimus engineers improved the design for higher force output and lower stroke output by optimizing the key design parameters to increase force instead of a balance of force and stroke. The same design parameters can be optimized for applications that are focused on: Force Stroke Speed Lifetime Power Consumption Weight Size The following video demonstrates the HASEL actuator optimized for force in comparison to the standard HASEL actuator with the same form factor. Please contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com to learn more. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Improving Distribution Center Sustainability: HASEL Actuators in Accumulation Conveyors
Warehouses and distribution centers operate around the clock processing immense volumes of goods. The energy costs to support these operations are huge in both monetary and environmental terms. Due to the constant operation and scale, even small efficiency improvements can significantly reduce operating costs and carbon emissions. As warehouses and distribution centers seek more sustainable operations, traditional pneumatic (air-powered) systems are under scrutiny. Large-scale pneumatic systems are inefficient, loud, leaky, troublesome, and very difficult to optimize. This results in enormous electricity usage and an opportunity for massive cost savings and sustainability improvements. Large compressed air systems are some of the most environmentally and economically expensive power systems in a plant, with efficiencies as low as 10-15% (U.S. Department of Energy: Energy Tips - Compressed Air, August 2004). In comparison, electrical systems can be as high as 80% (British Fluid Power Association: New developments and new trends in pneumatics, FLUCOME key-note lecture 2000). Pneumatic power is a century-old technology, and its limitations struggle to meet the expectations of 21st-century warehouses. Worker safety is paramount, yet the large compressors that supply entire distribution centers emit dangerously high levels of noise. Air lines are notoriously leaky, wasting energy and requiring overdesigned compressors. Additionally, air systems offer minimal connectivity options, meaning that separate sensors are required for diagnostics, or maintenance teams have to search large sections of conveyors to find and resolve problems. These challenges, coupled with sustainability improvements and operating costs reductions, are motivating many fulfillment centers to convert to electrical systems. While many pneumatic components have a direct replacement electric component, accumulation conveyor actuators have historically been limited to pneumatics. However, new HASEL electric actuators from Artimus Robotics offer an electric alternative to pneumatic accumulation conveyor actuators. HASEL actuators operate silently and have integrated intelligence supporting connected communication with Warehouse Management Systems. These actuators are inexpensive as scale, offer quick changeout (minimum downtime), and have analog control. The following video demonstrates the new HASEL actuators as smart electric alternatives for accumulation conveyor actuators. Please contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com to learn more. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Video Demonstration of Self-Sensing
HASEL actuators from Artimus Robotics are capable of self-sensing. These actuators are deformable capacitors, so measuring capacitance changes reveals information about the actuation distance, or stroke, during operation. This means that HASEL actuators are smart actuators since they are able to provide real-time information about their state and function. Closed-loop control of the actuator is also possible. For a detailed explanation of how self-sensing works for HASEL actuators, please see this post. The self-sensing capabilities of HASEL actuators bring a variety of benefits including: Operation in either force or displacement-controlled methodologies Information about the health or operating conditions of the actuators (example: failed vs operational) Information about the task and environment the actuator is operating in (examples: grip confirmation, actuation confirmation, system confirmation, and user or object behaviors and properties) Additionally, Artimus Robotics has developed a multi-channel sensing technique that can monitor the capacitance of multiple actuators simultaneously. The following video demonstrates how a HASEL actuator also works as a sensor. Please contact Artimus Robotics at info@artimusrobotics.com with any questions regarding self-sensing. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- Artimus Robotics Profiled on Company Week
Artimus Robotics cofounder and CEO Tim Morrissey recently sat down with the Company Week, the media voice for modern manufacturing, to discuss how HASEL actuators are helping the manufacturing and industrial automation Industries. In this interview, Tim discusses the various aspects of HASEL actuator that contribute to modern industrial automation such as electrical control, intelligence, and silence. Head on over to company week to read the entire article. https://companyweek.com/article/artimus-robotics
- Introducing Soft Grippers from Artimus Robotics
Demand for robotic automation is rising due to a decreasing supply of labor and a simultaneous increase in consumer demand. A critical component for a robot is the gripper – the part that interacts with objects and serves as the robot’s “hand”. While grippers have proven to be successful for many repetitive and simple tasks, a continuing challenge is creating a gripper with a high level of dexterity, adaptability, and sensitivity. This challenge is especially true for applications in agriculture, food processing, and e-commerce where objects vary in size and shape, are delicate and easily damaged, or change shape under the force of a gripper. Artimus Robotics is excited to introduce electrically-controlled soft grippers which provide controllable, fast, and sensitive gripping for a range of objects. Using HASEL actuator technology, these grippers respond quickly for fast cycle times in pick and place applications. The soft structure of the grippers from Artimus Robotics easily conforms to a variety of shapes to provide a secure yet delicate grasp of objects. Additionally, the gripping force is controlled by a variable input voltage to ensure a good grip while also preventing damage. Finally, HASEL actuators can simultaneously act as sensors, which allows these grippers to detect contact with an object, determine if an object is slipping, or infer information about the properties of the object being gripped, such as stiffness. The combination of these benefits translates into a soft electric gripper that is capable of automating a variety of tasks that are difficult for rigid grippers and pneumatic soft grippers. Intelligent, electric, soft gripper video - Agricultural Intelligent, electric, soft gripper video - Assorted Hardware What is a gripper? Grippers, also called end-effectors, end-of-arm tooling, or robotic hands, are the part of a robotic arm that interacts with objects. If comparing a robotic arm to a human arm, the gripper is equivalent to the hand of a human. The gripper is what does the grasping function and contacts the object to be gripped. Where are grippers used? Automated grippers are commonly used for pick and place tasks in industrial automation applications or food packaging. Grippers can also be manually controlled for exceptionally delicate tasks, such as surgical procedures or handling explosives. What are the challenges for grippers? It is common to see grippers that have been designed for repeatedly handling a specific object that is in the same orientation and is often made from rigid materials. An example of this is loading and unloading identical parts on a CNC machine. However, emerging applications for robots require automating tasks that are not as well defined and that require robots to handle a variety of objects. Industries such as agriculture and e-commerce are looking for robots that are capable of performing tasks that require human-like dexterity and sensitivity. A shortage of labor and an increase in demand has been driving the urgent need for automation in new use cases. In general, robots work very well in controlled environments doing repetitive tasks. However, in order to realize the full potential of robots, we need machines that can work in changing environments and interact with objects that vary in shape and size. A big challenge to this is in the vision and path planning - robots must find the target object and find the best way to get it. Many companies are working on this problem due to the recent developments in vision and machine learning. Another challenge is on the hardware side of this problem. A key component for achieving these capabilities will be grippers that have the dexterity to handle a wide variety of objects, especially those that are delicate or have irregular shapes. Most grippers are driven by motors and designed to pick a single, consistent object. However, most of the tasks that would benefit from a robot, such as to combat labor shortages, require handling a variety of object shapes and sizes. For example, consider the versatility required in agriculture to pick and handle produce, or in manufacturing, sorting the mixed variety of products on production lines. These objects exhibit a wide range of variability in size and shape, and can be fragile or squishy to touch. In order for a robot to be useful in assisting these applications, the gripper must be versatile enough to handle these variables. What is unique about HASEL for grippers? Several companies are exploring soft grippers to address the challenges listed above. Unfortunately, traditional soft gripper technologies simply are not versatile enough to solve the dexterity and environmental problems. Pneumatic soft grippers are slow, unintelligent, and have limited control. Vacuum grippers can’t grip meshed or non-flat/irregularly shaped objects, and suction areas can damage delicate objects. These traditional soft grippers have limited deformation modes and struggle to grip complex shapes. They are unable to adapt to the object and can not conform to its surface, limiting the amount of surface area contact. This requires more force to compensate, which can damage the objects. HASEL technology can satisfy the requirements of soft gripper applications. HASEL actuation is based on electrostatic principles, resulting in simple, reliable, and long-lasting designs. These soft grippers are highly compliant and adapt to the shape and size of the object. The high conformability gets more surface contact on the object with a solid but delicate grip compared to other soft grippers. HASEL technology also has built-in intelligent self-sensing capabilities which allow for grip force monitoring and closed-loop control, in addition to simple grip confirmation. These grippers are electric powered so the grasp time is very fast, and they can grip meshed and porous objects. Soft grippers from Artimus have analog control and manage good grasp strength with delicate gripping force. Artimus Robotics is developing artificial muscles, and the soft, intelligent grippers are state-of-the-art when it comes to replicating the functionality of the human hand. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- How quiet are HASEL actuators?
Silent actuation is a key benefit of HASEL actuation technology for applications that are sensitive to noise. Typical electromagnetic and pneumatic actuators generate a significant amount of noise. The lack of pneumatic noise, moving components, and motor whine makes HASEL actuators noiseless compared to pneumatic and electromagnetic linear actuators. Sometimes the noise of electromagnetic and pneumatic technologies can be reduced with additional noise-dampening system designs or components, but inherent differences in the technologies and actuation mechanics make HASEL actuators an ideal option for truly silent operation. The video below shows a comparison between pneumatic actuators, electromagnetic actuators, and the HASEL electrostatic actuator. Traditional linear actuators are complex and consist of many moving parts that generate noise. Below is a summary of the noise source by technology. Pneumatics For pneumatic actuators, a lot of noise comes from a variety of pneumatic system components. The compressor that provides compressed air to the pneumatic actuator is usually the loudest component because it generates so much mechanical noise. Compressors have motors, bearings, seals, pistons, diaphragms, rods, crankshafts, cylinders, and valves, which all independently emit noise. In large-scale industrial environments, one or two massive compressors supply all the compressed air for the entire building. The supply of a big building requires a lot of output from these large compressors, and they generate a lot of noise during operation. Other industries, such as medical devices or automotive, often have a smaller local compressor that supplies compressed air to an independent system. However, these compressors and pumps still generate noise, and the closer proximity to the user requires more noise-mitigation considerations from the designers. Other pneumatic system components, such as regulators, valves, dryers, and filters also emit loud sounds as they operate with compressed air. If the pneumatic system design requires venting, the vent itself can be extremely noisy as there is an abrupt blowing noise of the compressed air quickly expanding as the vent releases. There can also be noise from the actuator slamming into the end of its travel, depending on the type of pneumatic actuator. Overall, the noise generated by pneumatic systems can vary from major safety concerns (if people are near loud industrial compressors) to user experience issues (if the noise from the product is disturbing the users). Even if the product designers can mitigate the noise locally, such as with acoustic dampening foam, this will often create additional issues, such as heat transfer problems due to the pneumatic system overheating when densely packed in foam. Electromagnetics Traditional electromagnetic linear actuators, which use electric motors, operate using electromagnetic principles. The components required to facilitate the electromagnetic principles, such as the winding, rotor, bearings, air gap, and dynamic seals, all contribute to the noise of this type of actuator. The drivetrain makes noise too, such as the gearboxes to change the motor speed, and the lead screw or rack and pinion to translate to linear motion. Traditional electric linear actuators are complex and consist of many moving parts which generate mechanical noise. Since electromagnetic actuators can usually be identified by the distinct “whine” noise during operation, this can have detrimental effects on the application or users. If this noise is loud enough to be dangerous, then safety precautions, such as wearing earplugs, can reduce the ability of the operator to communicate or be aware of their surroundings. In other applications, this noise can reduce the effectiveness of the product, such as when stealth is needed for military applications. Finally, the noise can disturb the peace of users in consumer products or medical device applications. Electrostatics Specialty electric actuators made by Artimus Robotics are completely noiseless because the unique HASEL technology operates on electrostatic principles. There are only three components of a HASEL actuator and these do not have any mechanical or electrical noise. HASEL actuation is a soft material that changes shape so there are no moving mechanical parts to slide, rub, or roll. There is no “whine” noise and no mechanical noise from moving parts. Additionally, HASEL actuation is a closed system so there is no need for an external supply of compressed air and no pumping or venting of compressed air. The only noise emitted during operation is the thin polymer film changing shape during actuation. This can be heard if listening very closely in the video above. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.
- What industries use HASEL actuators?
Artimus Robotics is a component provider. Since the benefits of HASEL actuators apply broadly, Artimus supports a very wide range of industries. The industries with active implementation of HASEL actuators include: Industrial automation Automotive Medical devices Robotics Aerospace Undersea Defense Consumer products Many other industries are exploring HASEL actuators for potential use or are testing development kits from Artimus Robotics to streamline development and optimization for specific applications. Some multi-industry corporate partners are utilizing the Artimus Robotics Partnership Program to ensure exclusive access to HASEL technology across multiple industries. Please contact info@artimusrobotics.com to learn more. About Artimus Robotics Artimus Robotics designs and manufactures soft electric actuators. The technology was inspired by nature (muscles) and spun out of the University of Colorado. HASEL (Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing ELectrostatic) actuator technology operates when electrostatic forces are applied to a flexible polymer pouch and dielectric liquid to drive shape change in a soft structure. These principles can be applied to achieve a contracting motion, expanding motion, or other complex deformations. For more information, please visit Artimus Robotics or contact info@artimusrobotics.com.